REGARDING MY PERFORMANCE
REGARDING MY PERFORMANCE1. What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of?
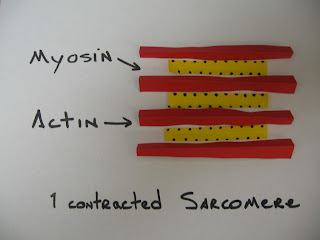
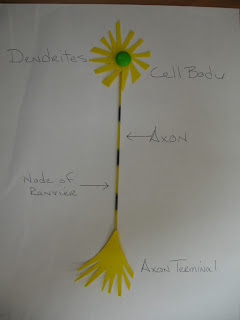
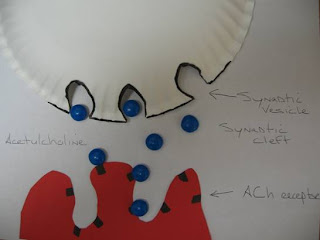
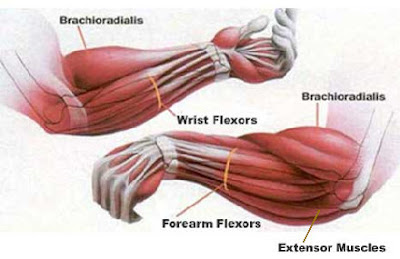
A. I really enjoyed the reproduction unit. I found if very interesting how we keep making babies.
B. The detail that Larry expects of us is a lot and now that I see what is expected I feel that I will be getting a good education.
C. I am proud that I have finished the class.
2. What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement?
A. Once again I wasn’t able to get all out of the internet links.
B. The demographics lab was not that easy for me and didn’t enjoy it.
3. What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit?
A. My overall grade is up to Larry, but I would like to see a B.
4. How could I perform better in the next unit?
A. I’ll will manage my time better, working full time is tuff but I need to finish this class.
REGARDING THE UNIT
At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course?
A. I was most engaged writing the compendiums, and the major unit lab.
At what moment unit did you feel most distanced from the course?
A. When I have been moving my home. Packing up during school doesn’t help with the studying.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit that find most affirming and helpful?
A. All of the effort the Larry has put into his home page. I just saw a lot of work put into my education.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing?
A. Trying to communicate is the toughest part of the class. I have questions and didn’t know how I was doing.
What about this unit surprised you the most?
A. I was really surprised with the amount of time we have spent in this class. And we are done, great job everyone.