

For this lab on building a working limb, I used house hold items that fit into my budget. The objective of this lab is to show the viewers how the human muscles work to move the body. This lab will explain the tissues, cells and nervous system of the human arm muscles and what goes on to make them move. 

The limb that I constructed is the human arm. The arm is to scale of an adult and consist of a one upper and lower skeletal bone and two muscles that will move it. The bones are made of extensions tubes off of a shop vacuum, and the muscles are rubber bands from my home gym. I used white tape to show how the muscle tissues are connected to the bones with tendons. The elbow joint is the end of a rubber hammer that was placed together with a vacuum tip, making a perfect hinge joint. The Red rubber band represents the bicep muscle and the green band represents the triceps muscle. When the red band is contracted the arm bends together. With the green band contracting and the red band relaxing the arm straightens out again. The hinge joint makes for a smooth movement and supports the two bones represented by the vacuum tubes. 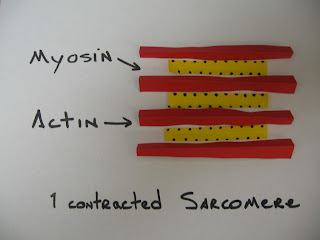



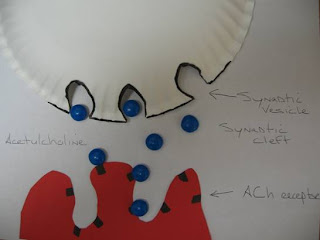
At the cellular level I have made the basics of the muscle fiber and how the muscle contracts. I also show how the nerve impulses travel and how the signal is sent to the muscle cell using action potential. To start off I made two slides of sacomeres, one in a relaxed state and another in a contracted state of position. Continuing to get smaller in scale I show the muscle fiber and how the Axon connects to the fiber so impulses can be sent. The impulses are sent by way of the neurons down to the muscle fibers, so I made actual neurons and its working parts. The impulse travel at high rates of speed to create responses and for the neurons to do this they use action Potential. I used my neurons to show its axon and how action potential travels so fast. Using the body’s sodium, potassium pump the positive and negative charges of the axon are change and the impulse travel by skipping over the myelin sheath which is called the salutatory propagation of action potential. Finally I made a slide and all of the part of the synaptic cleft of the muscle fibers. In this slide it shows how acetylcholine is used to pass the impulse at the synapse of the muscle fibers.
The impulses are sent by way of the neurons down to the muscle fibers, so I made actual neurons and its working parts. The impulse travel at high rates of speed to create responses and for the neurons to do this they use action Potential. I used my neurons to show its axon and how action potential travels so fast. Using the body’s sodium, potassium pump the positive and negative charges of the axon are change and the impulse travel by skipping over the myelin sheath which is called the salutatory propagation of action potential. Finally I made a slide and all of the part of the synaptic cleft of the muscle fibers. In this slide it shows how acetylcholine is used to pass the impulse at the synapse of the muscle fibers. 
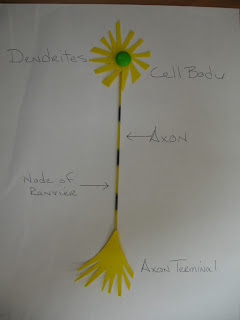
 The impulses are sent by way of the neurons down to the muscle fibers, so I made actual neurons and its working parts. The impulse travel at high rates of speed to create responses and for the neurons to do this they use action Potential. I used my neurons to show its axon and how action potential travels so fast. Using the body’s sodium, potassium pump the positive and negative charges of the axon are change and the impulse travel by skipping over the myelin sheath which is called the salutatory propagation of action potential. Finally I made a slide and all of the part of the synaptic cleft of the muscle fibers. In this slide it shows how acetylcholine is used to pass the impulse at the synapse of the muscle fibers.
The impulses are sent by way of the neurons down to the muscle fibers, so I made actual neurons and its working parts. The impulse travel at high rates of speed to create responses and for the neurons to do this they use action Potential. I used my neurons to show its axon and how action potential travels so fast. Using the body’s sodium, potassium pump the positive and negative charges of the axon are change and the impulse travel by skipping over the myelin sheath which is called the salutatory propagation of action potential. Finally I made a slide and all of the part of the synaptic cleft of the muscle fibers. In this slide it shows how acetylcholine is used to pass the impulse at the synapse of the muscle fibers. 

In summary the models I have created show from the cellular level to the actual action of the human muscles contracting and relaxing. The over all lab was fun and made me understand the concept of our bodies movement from the cellular level up to the actual muscle tissue.

No comments:
Post a Comment