Friday, June 27, 2008
SELF/UNIT EVALUATION
1. What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of?
A. The unit 2 lab was a lot of fun and I felt it came out the way I had planned.
B. My ethical essay has some good points and is all based on reality.
C. By in large the whole accomplishment of the unit is something to be proud of.
2. What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement?
A. My compendium reviews are not very interesting. I have now had trouble with them on both units. I just don’t learn well writing out my notes in an organized manner. I need to figure out a way make it less boring and a good study guide.
B. I should spend more time surfing the cool links that are provided.
3. What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit?
A. My overall grade is up to Larry, but I would like to see a B.
4. How could I perform better in the next unit?
A. Performing better on unit 3 is similar to the past units, I will show more interest in the internet based material and try to focus on my compendiums.
REGARDING THE UNIT
At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course?
A. I was most engaged working on and writing the unit lab.
At what moment unit did you feel most distanced from the course?
A. When I was working, I felt this pressure and couldn’t do anything about it.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit that find most affirming and helpful?
A. All of the help my crew gave me in getting all of my vitals and the pictures were great too.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing?
A. Trying to communicate is the toughest part of the class. I have questions and didn’t know how I was doing.
What about this unit surprised you the most?
A. I was really surprised with the relationship these chapters had with my work. The general nutrition and how we try and use those same ideas in the fire house. My job is based on all of the human systems that we covered.
ETHICAL ISSUE FOR UNIT II

Big population and big agriculture is the first reason that I will discuss. To sustain the populace of just this country let alone the world requires mass produced foods. The Food production for this country has gotten to be fast and efficient because the land and work force to produce natural, and community driven grown foods is more than this country want to handle. If you look at the population spread over the country you’ll see that the largest of populations are in cities and high industrial areas. They country has trade healthy food for businesses in industrial area. To supply these groups with food you have to grow and make foods that can be shipped to these areas. Shipping foods require you to add preservatives or time the growth of the croups to supply these areas. This poses a problem for the larger communities if there comes a time that foods can’t be shipped.
Lazy cultures have allowed for this kind of food production to continue to grow. People have been trying to make a fortune in this country since it began and as the opportunity has grown to make money the lack of interest in their health has diminished. As people became more specific in their trades or passions it has left few to make advancements in producing foods for the masses, not interested in growing it them selves. When a society is so driven in make a profit they tend to rely on someone to feed them. When that same person trying to feed everybody is also trying to make a profit the quality and quantity of foods will be dictated by that business. That’s why so much of the food is prepackaged and has a poor nutritional value.
Society has also made it a trend to go out and spoil ones self with fancy dinners or a quick bite mid day. If it was cool and easy to go out to you r garden or pasture and get your food everybody would be doing it, and striving to do it. We have become so focused on status that we have traded health for cultural status. If kids these days were more interested on how to irrigate a garden instead of irrigating their minds with video games, there might be a change in the way we view our food production industry in the future. It is just too easy to go and get fast food and get back to those trendy things that make you feel good about yourself.
Ultimately I see no change in the future of food production even with the big green trend and the emphasis of global warming. People just don’t care that much about how their food consumption is affect the future generations of this plant, or their fellow creatures. I think in the long run you are going to see a large number of the population dying off due to starvation, and only the wealth will survive, or those that know how to get their own food. The numbers on people that I think could really survive a mass food loss is small. That is probably a good thing for the planet, Mother Nature always gets through those problem times that the animals that inhabit her don’t. So, with the current populations, and focus on cultural status the cheap and easy way for food production is going to continue down the same path as it has been going.
Lab Project Unit 2 - Exercise Physiology

 Exercise Physiology
Exercise PhysiologyThe hypothesis for this lab is based on activities during a day at work. The question of a greater metabolic difference between the tones from alarm room or the actual fire calls has always interested me. I hypothesis that there will be an increase as each activity get more physically and mentally demanding.

The normal shift of a fire fighter starts at 0800 and continues for 24 hrs. During that time a fire fighter can have many different activities that they might perform. For this lab the four activities used will be a resting period, daily duties or work, being toned out for a call, and actual fire attack. The test subject will be an adult male, 28 years of age, weighting 185 pounds, in general good health.
The resting data will be collected during a resting period or safety break at approximately 1300. During that time the body can recover from calls or prepare for night calls. The metabolic rate at this time should be normal to low as to no extra energy is being required to work or think.
Duties around the fire house tend to be physically, yet still relaxing, and require more energy then resting. Duties like wash the fire trucks, mopping the bay floors, landscaping, and general cleaning can cause your body to increase its metabolic rate. The physical part of duties are not to challenging, but the mental part of trying to keep yourself interested in what your doing will affect it. That why fire fighters fool around so much.
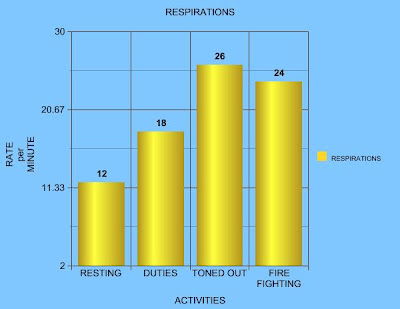
Tones happen during the day at an unknown time. This is a bit of an alarm and surprise so the body will have to increases its metabolism. This increase is to supply the body with its need oxygen and nutrients to go from a stand still to a rush. The demand on the body can increase when getting the gear on, and also the need mental capacity to make the right decisions on the incident start with the tones. That rush will become a greater demand when the tones are for a fire.
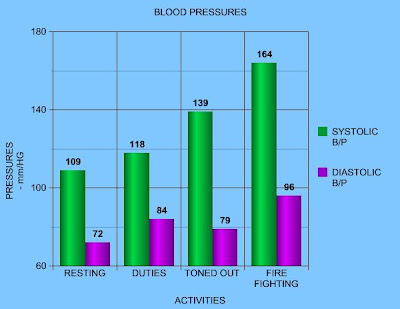
Fire fighting happens on rare occasion, but when it does the physical and mental requirements increase exponentially, you will see a major release of endorphins in response to the sympathetic nervous system. During that time, metabolic rate has become increasingly faster trying to match the demand of the cellular requirements. The results will be a pulse rate increase to supply the body with blood. The blood pressure increases to supply the tissues with oxygen and nutrients required to sustain aerobic metabolism. Respiratory rate also increases to supply the demand of oxygen on the heart, brain, and body. With the increased respiratory rate the body can also rid its self of carbondioxide and other by products in the blood stream.

The data was collected for this lab at the fire station that I work at. I was able to use the tools and medical equipment to collect detailed vitals on myself with the help of the crew. The ECG monitor was used for my vitals, it has a Bp cuff and pulse oximetry, I also was hooked up to the ECG and was able to see the change of my heart rhythms. They took pictures during different process, and times of the day. The resting, duties, tones data was collected at the actual times during the shift that they happened. Unfortunately, there were no fires during the shift, but we drill. During the daily drill evolutions I was able to simulate the activates of fire ground operations. We practice like we play, so it is very accurate, other then the mental component.


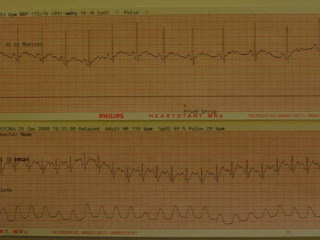 These ECG strips shows my heart rate and rhythm. The top strip is my heart during rest, a normal sinus rhythm. The bottom strip is after extreme physical out put, sinus tachycardia. The higher my cardiac output is the smaller and narrower the waves get. This shows how my heart is working to keep up with the metabolic demand of my body. The increase pulse rate will increase my B/P and require high oxygen intake, increasing respirations.
These ECG strips shows my heart rate and rhythm. The top strip is my heart during rest, a normal sinus rhythm. The bottom strip is after extreme physical out put, sinus tachycardia. The higher my cardiac output is the smaller and narrower the waves get. This shows how my heart is working to keep up with the metabolic demand of my body. The increase pulse rate will increase my B/P and require high oxygen intake, increasing respirations.Nutrition - Compendium 4

Table of Content
The Digestive Tract
Overview
Stomach Small intestine
Large Intestine
Accessory Organs
Nutrition and Weight
The Digestive Tract
The process of digestion has four parts, ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination.
The process starts in the mouth were chewing a mechanical digestion starts to break down the food.
The food travels down the esophagus and into the stomach. The stomach mixes in acidic juices to break down the food more. The food mass moves into the small intestines were more juices are introduced breaking down the mass for absorption. Nutrients are absorbed by the walls of the small intestine.
The large intestine absorbs the last bit of water and vitamins out of the feces; the large intestine is responsible for carrying out waste.
Accessory organs that play a part in the digestion process are pancreas liver, and gallbladder.
The pancrease produces juices that dissolve proteins, carbohydrates, fats.
The liver is the body’s main filter; it takes out old blood cells and other waste out of the blood stream. I stores and breaks down glycogen, for glucose use.
Nutrition and Weight
The essential amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, fats all play a role in the balance diet. Carbohydrates break down into glucose for energy, but simple sugars tend to be stored as glycogen and lipids. The simple absorption of the sugars cause a fast release of insulin and over time can cause diabetes. Proteins supply the amino acid used. Fatty acid come in two types saturated and unsaturated. Unsaturated fatty acids can help cardiovascular systems, while saturated usually causes poor heart out put.
Nutrition: Onlin Lab
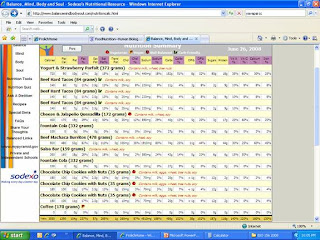
This is a very poor diet, and I should be embarrassed. It just so happened that the day I did this Lab I was working on a job site and short on cash. It is very convenient and quick to run to Del Taco and grab a combo. The food is okay but I know it is bad for me. That night I went out with a friend and Alfonso’s sounded good. The overall caloric intake for that day is way over what my norm intake should be.
2. What would you change about this day's eating, if anything?
I would have to change all of it. The issue is poor planning on my part and I didn’t pack a lunch to take with me. I have healthier food at home and just need to prepare before I go to work. That night was a treat for me and I could have eaten better at home. When you think about the food and look at the charts and the nutrition guides it is kind of disgusting.
3. Do you find this kind of nutritional tracking helpful? Why or why not?
Like the main issue of a poor diet, the nutritional guide is just an inconvenience if you don’t plan on setting time aside to use it. It can be very helpful in managing your diet and I would like to try and use it in the future. Shopping for the health foods is another scheduling issue and just needs some proper planning as well.
Oxygen/Microbes/Immunity - Compendium 3
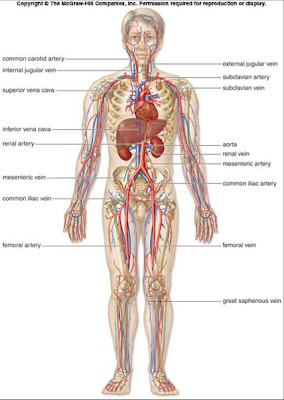
Table of Content
Chapter 5
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Vessels
Blood Vessels
Arteries
Veins
Capillaries
Left side
Right side
Heart beat
Pulse
Blood pressure
Capillaries Exchange
Capillary pressures
Disease
Hypertension
Diet
Chapter 6
Blood
Function
Red Blood Cells
Function
O2 transport
White Blood Cells
Function
Granular Leukocytes
Angranular Leukocytes
Platelets
Clotting
Blood Typing
Grouping
Type A
Type B
Type AB
Type O
Agglutination
RH Groups
Homeostasis
Systems working together
Chapter 7
Microbes and Pathogens
Bacteria
Viruses
Lymphatic System
Primary Organs
Secondary Organs
Defenses
Nonspecific
Specific
B cells
T cells
Chapter 5
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart and blood vessels.
The heart pumps the blood through out the body in the blood vessels. The blood vessels carry need nutrients and gases to the capillary beds were exchange of fresh nutrients and gasses are taken by cells and used while waste is taken away and removed from the blood stream.
Blood Vessels
Arteries are thicker walled vessels that carry blood under higher pressure away from the heart.
Veins carry blood towards the heart under low pressure, using valves to keep blood flowing in one direction.
Capillaries are the smallest vessels were blood nutrients are exchanged for waste in between arteries and veins.
Pumping Blood
The heart pumps blood through out the body by using the left and right side of its structure.
Blood enters the heart into the right atrium and pass through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonary system to rid the red blood cells of its CO2 in exchange for fresh O2. The blood returns to the heart through the left atrium and passes through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps blood through the aortic valve and into the body under Pressure that is measured in millimeters of mercury.
The heart is stimulated by two nodes that cause it to contract. The Sinoatrial node (SA) starts off contracting the atriums and sending the pace to the Atrioventricular node (AV). The AV node causes the ventricles to contract.
The pulse is the rate the heart beats at.
Blood pressure is the measurement of the blood against the walls of the vessels during contraction (systolic) and during rest (diastolic).
Blood flow is under pressure in the arteries until it reaches the capillaries, it then losses it velocity for nutrient and waste exchange. The blood flows into the veins at lower pressure returning to the heart.
The cardiovascular pathways are broken into two circuits. The pulmonary circuit is blood flowing to the lungs for O2 exchange. The systemic circuit is blood flowing through out the body to all of the organs and cells.
Capillary Exchange
The arterial end of the capillaries the greater pressure causes water to leave the capillaries due to lower osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is greater on the venous end which allows the water to enter the capillaries. The water is picked up into the lymphatic system and returned to the blood on the venous side.
Cardiovascular Disorders
Cardiovascular disease in the number one cause in death in western countries. With atherosclerosis and hypertension causing stroke and heart attacks or vascular aneurysms. Keeping a health diet and exercising regularly can prevent heart disease.

Chapter 6
Blood
The function of blood is to transport nutrients, hormones, O2 to cells. Transport waste and CO2 from cells, fight and rid body of infections. Regulate body tempature, and control PH balance.
The plasma that makes up is 91% H2O, and is produced in the liver. Plasma regulates Osmotic pressure, transports and helps with clotting factors in vessels.
Red Blood Cells (RBC’s)
The release of erythropoietin causes the production of RBC’s.
The main function of RBC’s is transport of O2.
White Blood Cells (WBC’s)
WBC’s function is to combat disease.
Granular Leukocytes respond first to infection, sucking up unwanted substances.
Agranular Leukocytes are larger WBC’s and are for specific immunity
WBC’s have a life span of about 120 days
Blood Clotting
A platelets function is in clotting and come from red bone marrow.
Platelets and proteins in plasma combine creating fibrin threads which trap RBC’s and cause the clotting and blood stop.
Blood Typing
Determining the ABO group or presence or lack of different antigens.
Type A- Surface A, anti B antibodies
Type B- Surface B, anti A antibodies
Type AB- neither anti A or anti B antibodies, both A, B surface antigens
Type O- neither A, B surface antigens, both anti A, B antibodies
Agglutination- putting corresponding antigens and antibodies together
Homeostasis
This is very important with the cardiovascular system because it take make factors for the system to run smoothly. The heart just doesn’t need to pump the blood but the pulmonary system needs to provide the right amount of O2 and CO2 exchange. The digestive system needs to provide the proper nutrients, and the nervous and endocrine system needs to control the blood pressures to move the blood through out the body.
Microbes and Pathogens
Bacteria are cells the reproduce independently of possible host cells. The produce toxins and can reproduce inside of a host cell.
Viruses are proteins coated and cause a host cell to reproduce with their genetic code by taking over the cell. The new cells emerge with viral diseases which are tuff to combat.
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic vessels connect the system to the circulatory system.
The primary organs are the red bone marrow that makes the B cell, and the thymus glands were the T cells are made.
The secondary organs are the lymph nodes the clean waste out of the lymph, and the spleen that cleans the blood of debris.
Defenses
Two types of defense.
NON specific
Barriers and protective protein.
The inflammatory reaction.
SPECIFIC
B Cells and T Cells are the body’s defense to foreign and abnormal molecules.
T cells actually go out and destroy the cells.
B cells mark the cells or foreign cells to be recognized and destroyed.
B/P Online Lab
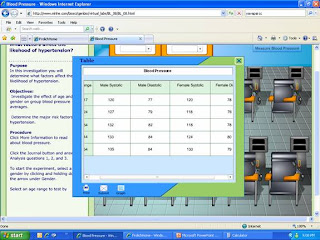
1. State a problem about the relationship of age and gender to blood pressure.
There are many factors that are related to blood pressure. The most prevalent and often the one that can’t be controlled, is heredity.
2. Use your knowledge about the heart and the circulatory system to make a hypothesis about how the average blood pressure for a group of people would be affected by manipulating the age and gender of the group members.
Blood Pressure (B/P) can be manipulated in males and females just by the genetic that they inherit. A person will also inherit their height and weight to a point which can affect B/P. With ones physical traits they might be more or less prone to exercise, which will affect the efficiency of their circulatory system. Those that don’t exercise tend to have a poor diet and might have increased sodium levels affecting their B/P. Age in both genders will affect the blood pressure also; as the body gets older the vessels lose their elasticity and can’t help regulate B/P. In younger ages the circulator system works more efficient and there is less B/P problems.
3. How will you use the investigation screen to test your hypothesis? What steps will you follow? What data will you record?
The steps that I will use will be orderly, starting with one gender and moving through the age group. As I move through the age groups I will key in on increased B/P, heredity and poor health by lack of exercise and sodium intake.
4. Analyze the result of your experiment. Explain any patterns you observed.
General B/P issues began to start in the older age groups, in both genders. With the increased age the weight and lack of exercise started becoming prevalent. In females I also noticed those same people had increased sodium levels. Heredity played some part in certain people but not as much as I thought it would have.
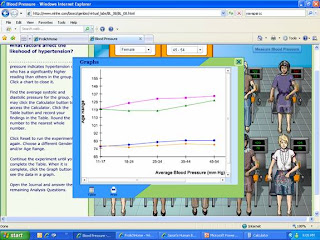
5. Did the result of your experiment support your hypothesis? Why or why not? Based on your experiment what conclusion can you draw about the relationship of age and gender to group blood pressure averages?
I don’t think so; I found that heredity took back seat to weight and poor exercise habits. In females the weight played a big part and with males the lack of exercise and poor weight played a part. Both genders had heredity hypertension playing a part. As age increased these factors became more prevalent.
6. During the course of your experiment, did you obtain any blood pressure reading that were outside of the normal range for the group being tested? What did you notice on the medical charts for these individuals that might explain their high reading?
Yes as the age groups got older the B/P’s consistently got out of normal range. Only in a few cases, but it was enough to be noticed. Those people tended to be in poor shape and had increased weight, plus some heredity.
7. List risk factors associated with the hypertension. Based on your observation, which risk factor do you think is most closely associated with hypertension?
The weight of people and their medical history.
8. What effect might obesity have on blood pressure? Does obesity alone cause a person to be at risk for high blood pressure? What other factors, in combination with obesity, might increase a person's risk for high blood pressure?
General cardiac out put is affected due the weight that the heart and body have to support. The lack of exercise due to the weight, and poor eating habits which cause the increased weight play a role in hypertension. Other diseases that cause or affect B/P such as diabetes are seen in over weight people, and can cause poor health with risk of high B/P.
Friday, June 13, 2008
SELF/UNIT EVALUATION
1. What were the three aspects of the assignments I've submitted that I am most proud of?
A. I would have to say that I am proud of completing this first unit, and I had to work at it.
B. The detail that Larry expects of us is a lot and now that I see what is expected I feel that I will be getting a good education.
C. By in large the whole accomplishment of the unit is something to be proud of.
2. What two aspects of my submitted assignments do I believe could have used some improvement?
A. My project could have been bigger, more detailed. I got a lot out of it and learned a lot.
B. I should spend more time surfing the cool links that are provided. I looked at most of them but wasn’t able to really absorb what I wanted.
3. What do I believe my overall grade should be for this unit?
A. My overall grade is up to Larry, but I would like to see a B.
4. How could I perform better in the next unit?
A. I’ll will manage my time better, working full time is tuff but I need to finish this class. I also want to take better notes for my compendiums.
REGARDING THE UNIT
At what moment during this unit did you feel most engaged with the course?
A. I was most engaged writing the compendiums. Never had an assignment like that before.
At what moment unit did you feel most distanced from the course?
A. When I was working, I felt this pressure and couldn’t do anything about it.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit that find most affirming and helpful?
A. All of the effort the Larry has put into his home page. I just saw a lot of work put into my education.
What action that anyone (teacher or student) took during this unit did you find most puzzling or confusing?
A. Trying to communicate is the toughest part of the class. I have questions and didn’t know how I was doing.
What about this unit surprised you the most?
A. I was really surprised with the amount of work that needed to be put in just to get the assignments done. I will definitely prepare better next week, starting now.
ETHICAL ISSUE FOR UNIT I
 The beginning of the term “genetics” came about around 1909, and with small effect on the biological studies of human behavior. Systematically studying biological behavior and more closely human behavior had begun hundreds of year prior. Looking into what make humans and other closely relate animal behave the way they do. It was always difficult to define and explain behavior but with the announcement in early February 2001 of the human genome being completely mapped brought new possibilities in find out what make us tick the way we do. When comparing behavioral genetics with heredity and environmental influence the confliction is apparent and difficult to side with.
The beginning of the term “genetics” came about around 1909, and with small effect on the biological studies of human behavior. Systematically studying biological behavior and more closely human behavior had begun hundreds of year prior. Looking into what make humans and other closely relate animal behave the way they do. It was always difficult to define and explain behavior but with the announcement in early February 2001 of the human genome being completely mapped brought new possibilities in find out what make us tick the way we do. When comparing behavioral genetics with heredity and environmental influence the confliction is apparent and difficult to side with.The human genome has about 30,000 genes that make up about 250,000 proteins. These proteins transcribe over to the cells to metabolize in fashion for the cells task at hand. In the human DNA 95 percent of it doesn’t even code for these proteins. The view of the human genome currently is it’s 30,000 genes aren’t complex enough to in fact influence behavior. Behavior like other traits carried by humans take multiple genes to influence them and not very much evidence is there to surround it. So, the ethical question is to continue studying and putting forth the money or place it by the way side.
Heredity is all based on the genetics passed down from one generation to another. A yellow Labrador instinctively knows how to retrieve, as does a border collie know to herd its stock. Do the genetics passed down from generations, coded in the DNA tell them what to do, or something else? If science is use to influence these genetic what is the reason they can’t be enhanced. There still is found to be a link in some genes to effecting mentation, aggression or criminality. If found to be true that a humans behaviors are pre-patterned in their DNA, that would have huge affects on our society. Environmental influence is still to be argued what makes humans behave. The DNA can only place code to get everything moving. It is up to society and then personal life experiences to create the behaviors. That can be a problem when faiths believe in a more divine creation and would have large ethical issues to deal with it.
The advancements of science are surely breaking new ground in genetics. The influence of society has and will greatly effect how far it can go. Government has started to show interest with legislation and state law. The behaviors of humans are still and will be an issue. While it is still undetermined were behaviors build from, the genetic study can continue to use scientific theory to help understand it better. It is getting easiler to show the distant relationship between biology and behaviors of humans. It may someday show us a better world.
Lab Project Unit 1 – Animal Cell
 For this lab project I made an animal cell. Since I’m a poor Biology student I use common goods found in my house. I started by placing the different goods out to see what might best represent the different pars of the cell. These are what I came up with.
For this lab project I made an animal cell. Since I’m a poor Biology student I use common goods found in my house. I started by placing the different goods out to see what might best represent the different pars of the cell. These are what I came up with.Nucleus- I used an egg cut in half, this was a good representation because the yoke looked like the nucleolus inside of the nucleus.
Endoplasmic Reticulum- I used silver rope bunched together.
Mitochondria- The red pepper I used because the shapes were similar.
Lysosomes- The yellow peppers also fit the mold.
Golgi- I used small onions due to the fact that the inside of the onion have different layers.
Vesicles- These small little storages and transporter were represented by the small seeds in my cell.
Cytoplasm- I used the basis of all life, and since most of a cell is made of it. Water dyed.

The cell membrane and all of its organelles where placed on a plate. The over all look was some what goofy and I feel that our cells are probably the same, but much more organized. The over all experience was difficult because of the budget and what was expected. To represent the basics of all life and make the statement of knowledge of it came to me as a challenge. I have learned much of the cellular structure and it methods, below is a more detailed description of what I have learned.

My Animal cell
The basic parts of my cell are made up of --------- as shown in the picture. The parts represent the cells different working parts as labeled.
Nucleus
-Nuclear envelope, protection and covering of nucleus.
-Nucleolus, produces subunits of ribosomes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
-Rough ER, studded with Ribosome’s
-Smooth ER, synthesizes lipids
Mitochondria
-An organelle
-Carries out cellular respiration.
-Produces ATP molecules during process, our energy.
Lysosomes
-Cellular (garbage men)
- Digest macromolecules, and dead cell parts.
Golgi
- modifies cellular products
-Process and package
Vesicle
- Sacs in the cell that store and transport substances.
Cillia
-Propel cell around with fluid like motions.
Cytoplasm
- Fluid outside of nucleus that contains organelles
Animal cell Mitosis
Using these general objects I can show how an animal cell during the phases of Mitosis divides.
The Prophase begins the process as the cells nucleolus disappears and the new duplicated chromosome begin to move apart. The cell itself begins to for a spindle for the chromosomes to attach too.
The metaphase allows the centomeres of the chromosomes to attach onto the spindle fibers. The spindle poles have moved to opposite side in the cell. The chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
The Anaphase starts to pull apart the chromosomes and now the sister chromatids move towards the poles. The new sister chromosomes match that of the parent cell and can continues passing on genetics.
The Telophase starts to envelope a nucleolus around the chromosomes. Cytokinesis begins to separate and make sister cells complete.
DNA Replication
- DNA and Proteins are contained in the cell nucleus.
- Chromosomes are the condensed and organized DNA and Protein.
-DNA is a double helix stand of information.
-The information can be split and passed on.
-When DNA splits the template pairing the Nucleic acid OF the DNA with strands of RNA.
-mRNA carries the genetic codes to ribosome’s to translate and synthesis proteins
-Proteins are synthesis two ways.
-Transcription, enzymes break the DNA double Helix and RNA join to the complementary bases. mRNA is now formed, the same genetic sequence as the DNA.
-Translation, takes place in the ribosome. RNA molecules and amino acids are synthesized allowing the ribosome’s to make proteins based on the genetic code.
- The DNA code is then regulated by gene expression and work toward Homeostasis.
During this lab project and Unit 1 I have been able to grasp the concept of the cells that make up the world. This very complex life is the foundation of my scientific education. Learning how the cell divides and what all of its components do to create life has been a bit challenging. I feel that with this base knowledge I will be able to further my education in human biology.
Genetics – Compendium 2
Chromosomes
Cell Cycle
Mitosis
DNA’s role during Mitosis
Gene expression
Cancer Cells
Genetic traits and Meiosis
Alleles
Chromosomes
- Chromosomes which are contain inside of the cell nucleus.
- The human nucleus contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. Totaling 46 chromosomes.
- 22 of these pairs are known as autosomes, which carry genes traits having nothing to do with sex of the individual.
- 1 pair contain genes that determine individual sex
- Males have the pair of X and Y
- Female has the pair of X chromosomes
Cell Cycle
- Two cycles of the cell occur continuously
- Interphase, during which normal cell function is happening.
- Interphase is also when the cell prepare for division, lasting about 20 hours or 90% of the cell cycle.
- Cell division has two stages
- Mitosis, nuclear division with two identical sets of chromosomes.
- Cytokinesis, division of cytoplasm
Mitosis

-Duplication division assures that cell chromosomes are in the same amount and kind.
- Phases of Mitosis
- Prophase, Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers.
- Metaphase, Chromosomes align at the equator
- Anaphase, Chromatids separate, and now chromosomes move towards poles.

-Telophase, Nucleus develops around chromosomes, cytokinesis begins.
- Mitosis is critical for growth and tissue repair.
DNA’s role during Mitosis
- DNA is replicate and passed on to daughter cells
- DNA information from parent cells is transcribed into protein that will run daughter cells metabolism.
- DNA is a double helix that can separate and transcribe to other half mRNA.
- mRNA then translates into amino acids that fold up to build proteins.

- Ribosome’s translate mRNA and make proteins
- These proteins effect and cause cell metabolism.
Gene expression
- Gene expression is regulated
- Cell feed back is how regulations controls metabolism
- Lack of cell regulation caused problems with gene expression.
- Cancer can be the outcome.

Cancer Cells
- Characteristics
- Abnormal size nuclei
- Abnormal amount of chromosomes
- Abnormal amount of chromosomes allows cell to divide repeatedly and continue doing so.
- Cancer cells can form tumor
- Cancer cells aren’t encapsulate and can spread to surrounding tissues
- Cancer can be caused by genetics heredity, environmental, carcinogens, and poor diet.
- Cancer is a genetic disease.
Genetic traits and Meiosis
- During meiosis gametes are formed having all possible combinations of parent chromosomes.
- During fertilization complete chromosome recombination occurs and mitosis can begin with a full set of 23 pair chromosomes.
Alleles
-During meiosis small variations in the DNA and chromosomes protein coding cause Alleles.
- Hereditary traits for the mother or father are passing to the zygote by the combination of these Alleles at particular gene or chromosome regions.
- These sometime dominate traits give us an advantage in survival.
- With this advantage or disadvantage, the basis of evolution’s natural selection.
Genetics: Online Lab


The second web lab was based on the Punnett Square. In this lab we were using fruit flies. Using the Punnett Square we adjusted the genotype and phenotypes of the flies to figure out what off spring we would get. If you choose the wrong parents then the off spring would match. Scenario 5 was fun so I went and did all of the other ones. I lost my first page and had to do five over again, but it was easier after I did the other ones. In the end I got good at it and learned something about inheritance.
Genotype- The alleles the make an individual.
Phenotype- The alleles that determine the physical characteristics
Allele- Genes have the same position on the chromosomes and affect the same traits.
Cross- Having to do with the inheritance of the alleles one or two crosses can happen. This will determine what traits the off spring inherit.
Dominant- These traits are shared by both parents and alleles of the kind get past on more often. These are represented by upper case letters.
Recessive- These traits are given the same letters represented in lower case. These alleles don’t get passed on as much but still can be inherited.
Cells – Compendium 1

Chapter1
1.1- Fundamentals of life
1.2- Human relations with all living things
1.3- Using the scientific Process
1.4- Scientific studies and understandings
1.5- Responsibilities in science and society
Chapter 2
2.1- The foundation of life at it’s smallest
2.2- H2O’s importance
2.3- Molecules
2.4- Carbohydrates
2.5- Lipids
2.6- Proteins
2.7- Nucleic Acids
Chapter 3
3.1- A cell
3.2- Cell organization
3.3- Cellular wall
3.4- The Nucleus and protein production
3.5- Cytoskeleton and movement
3.6- Mitochondria
Chapter 4
4.1- Tissues
4.2- Connective tissue
4.3- Muscular tissue
4.4- Nervous tissue
4.5- Epithelial tissue
4.6- Cell junctions
4.7- Integumentary System
-Organisms on the plant share many commonalities, and have structure.
-The levels of structure are atoms, molecules, cells, tissue, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biosphere.
- Organism characteristics are reproduction, growth, development, response to stimulation, have history and adapt to life.
1.2
- Living things are classified by their evolution
- Humans are in the Animalia kingdom
-Humans have developed advanced brains
- Stand up right
- Speak creative languages
- Use tools
- Humans have created a deep heritage and now affect the whole Biosphere.
- Humans need to take care of the biosphere and their mark upon it.
- Humans depend on the biosphere
1.3
- Knowing how to take care of the biosphere takes information
- Information of the natural world is gathered with the scientific process.
- Scientific Process is making and observation, forming a hypothesis, experimenting, and observing. Then making a conclusion, and writing a scientific theory.
- Controlled studies use the experiment of placing subjects under the same treatment, but a portion of the group is not actually exposed to the variable. Once the study is complete the finding are published in a scientific journal.
1.4
- Not all date has true outcomes.
- Anecdotal and Correlation data has small support and needs more data.
- The use of statistical date tells us how trustworthy results of a study are.
1.5
- Scientific information is based off of studies that are observed and experiments that lead to theories.
- The general society needs to comprehend these studies and come to their own feelings.
- Now that technology is advancing and become more apart of the world, one need to understand and study to come to decisions on its use.
2.1
- Matter takes up space and has mass.
- Matter can be in 3 forms, solid, liquid, or a gas.
-Elements have one type of atom.
- Elements can’t be broken down.
-Atoms have weight, that weight is based on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
- Atoms react to each other and form ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
2.2
- At room tempature water is a liquid.
- During heating or freezing process water is slow to change tempature allowing more consistency between changes.
- Water is the universal solvent due to its polarity
- Water has a natural pH, acids and bases change the pH of water.
- Molecules that sustain life are Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids.
2.4
- Carbohydrates can be simple or complex.
- Simple Carbohydrates are monosaccharide or disaccharide.
- Complex Carbohydrates are polysaccharides
- These carbohydrates are what glucose is created from.
- Plants store glucose as cellulose and human digestive system can’t break it down.
- Animals store glucose as glycogen.
2.5
- Lipids are stored for long term energy.
- Fats and oils are broken down into fatty acids.
- Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated.
- Cellular wall are made of phospholipids this allows for molecules to move in and out of the cell.
2.6
- Proteins are important in the structure of cells
- Proteins have many jobs accounting for movement muscle contraction transport of molecules in blood.
- Protein is macromolecules and is essential to life.
2.7
- Nucleic acids or DNA, RNA.
- DNA is double stranded and forms a helix
- RNA is not formed in a helix
- ATP is an energy molecule
- Cells are the basic units of life.
3.2
- Cells have a structure of a plasma membrane and a central nucleus.
- Cytoplasm fills the cell and organelles move in the cytoplasm do the specific jobs.
- Organelles in the cell are Mitochondrion, Golgi apparatus, vesicle, lysosome, centrioles.
3.3
- The Plasma membrane regulates the passage of molecule in and out of the cell.
- Passage of molecules can be passive or active.
- Passive requires no energy.
- Active requires energy
3.4
- Nucleus houses the cells DNA and produces RNA
- Nucleus chromatin condenses and become chromosomes at cell division
3.5
- The cytoskeleton uses microtubules and actin filaments to hold its structure
- The cilia and flagella on the outside move and propel the cell.
3.6
- Mitochondria have evolved to give respirations to the cell, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
- During this respiration the mitochondria create energy in the form of ATP.
- Four group of tissues
- Connective, Muscular, Nervous, Epithelial.
4.2
- Connective tissue comes in four groups.
- Loose fibrous, adipose tissue.
- Dense fibrous, tendons and ligaments.
- Cartilage and bone.
- Blood.
4.3
- Muscular tissue comes in three groups.
- Skeletal, smooth, cardiac.
- Cardiac and skeletal are striated.
- Cardiac and smooth are involuntary.
- Skeletal muscle attach to bone.
-Smooth muscle makes up internal organs.
- Cardiac muscle makes up the heart.
4.4
- Nervous tissue is composed of neurons
- Each neuron consists of dendrites, cell body, Axon, and conduct impulses.
4.5
- Epithelial tissue covers the body
- Types are Squamous, Cuboidal, and Columnar.
4.6
- Cell junctions have three types
- Tight junctions fasten cells.
- Adhesion junctions allow cells to stretch and bend when together.
- Gap junctions allow molecules and signals to pass between cells.
4.7
- Integumentary system consists of skin and its accessory organs.
- Skin has two regions.
- Epidermis exposed
- Dermis internal
- Subcutaneous internal
4.8
- Different organs create the systems and can be found in different locations.
- Organs work and survive together as a system
4.9
- That system need to be in homeostasis for survival.
- Homeostasis is the relative constancy of the internal enviorment.
Thursday, June 12, 2008
Cells: Online Lab
 The foundation of Biology 156 starts with the first lab. The knowledge and use of the microscope. Without this complex tool for the time of its invention, the scientific world might not have advanced in the manner it has. For, a great view into our microscopic world, the microscope is used on these basic concepts.
The foundation of Biology 156 starts with the first lab. The knowledge and use of the microscope. Without this complex tool for the time of its invention, the scientific world might not have advanced in the manner it has. For, a great view into our microscopic world, the microscope is used on these basic concepts.One should grab the microscope by its Arm, and support it under its base. Place it on a level solid table, having the arm towards its user. Using the larger knob for course movement, adjust the microscope’s body tube to its furthest resting point from the stage. Adjust the nosepiece so its low-power objective lens is over top the hole in the stage and it clicks into place. The diaphragm can now be moved as one looks through the eyepiece putting the circle of light centered to the hole in the stage. Now it’s ready for viewing. Place your slide on the stage, centering up the specimen. Place stage clips on slide when in place. Looking at the stage from the side use the course adjusting knob move the low-power objective lens towards the stage almost kissing the slide. Now looking through the eye piece, adjust the course knob until specimen come into focus. From there one can move to higher power objective lens and then use the fine adjusting knob to bring the specimen into focus. Welcome to our microscopic world.
The Objective lenses are closest to your slide. These lens come in different magnification depending on you microscope. Your common magnifications are 100X, 40X, 10X, and 4X. The 4 power lens is used to start off at the beginning, so that you can focus you slide from a general view and then once in focus change magnifications. During focus of the 4X lens you can use the course adjusting knob. When magnification changes to 10X or greater you need to use the fine adjusting knob to focus. During your observation of just 4X you will have magnified the slide to that of the first microscopes, being use by their inventors. Now there is Dissection, Scanning Electron (SEM), and Transmission Electron microscopes (TEM) that are bring the microscopic world to us in 3-D.
Monday, June 2, 2008
Some interesting things about Nick Knowlton
1. School has never been interesting until I found my passion, that's why I'm here at 28 years old.
2. I have a huge attraction to our natural high, ADRENALINE.
3. The outdoors is a very big part of my life and spend as much time with her as I can.
I'd have to say my favorite artist is Shel Silverstein, I enjoy his view of the world, and his drawings have always put a smile on my face.



